Metal Biogeochemistry and Food Safety Lab (MBFL)
金属生物地球化学与食品安全实验室
金属生物地球化学
与食品安全实验室
Metal Biogeochemistry and Food Safety Lab (MBFL)
We need you!
欢迎学硕、工硕加盟我们实验室(环境生物专业),如有兴趣,请与钟老师联系。
zhonghuan@nju.edu.cn
2018年7月
"未来的实验室伙伴"你好!我们欢迎你作为环境生物方向的研究生,或是以博士后、助理研究员加入我们这个集体;作为一个国际化的实验室,我们会为优秀的你提供国际化的培养,你的工作场所可能位于中国、加拿大、美国、挪威等地,并有机会与世界各地的学者共同开展研究。你的背景可以是环境科学、生物、化学、地球科学、环境工程、食品科学、医学、中医学等相关学科,但更重要的是,你有足够的热情与兴趣和我们一起探索这个未知的世界,并有决心去迎接困难的挑战。
钟寰 博士
zhonghuan@nju.edu.cn
Dear future lab members,
We welcome talents who are interested to be graduate students/postdocs in our lab. Your background could be biology, chemistry, geochemistry, environmental engineering, food science, or medicine. As an international research lab, you will have opportunity to work with scientists from different parts of the world, e.g., China, Canada, US, Norway and may also work there. Are you prepared to explore the unknown world with us?
Dr.Huan ZHONG
zhonghuan@nju.edu.cn
研究方向
Research Areas

金属生物地球化学
Metal Biogeochemistry
Geochemical and biological factors affect speciation, bioavailability, and bioaccumulation of metals.

金属食物链传递与食品安全
Trophic Transfer of Metals and Food Safety
Transfer of metals through the food chain & Human exposure to metals through food consumption.
土壤修复
Soil Remediation
In situ remediation of metal-contaminated farming soils using novel techniques.
— 指导教师—
Principle Investigator
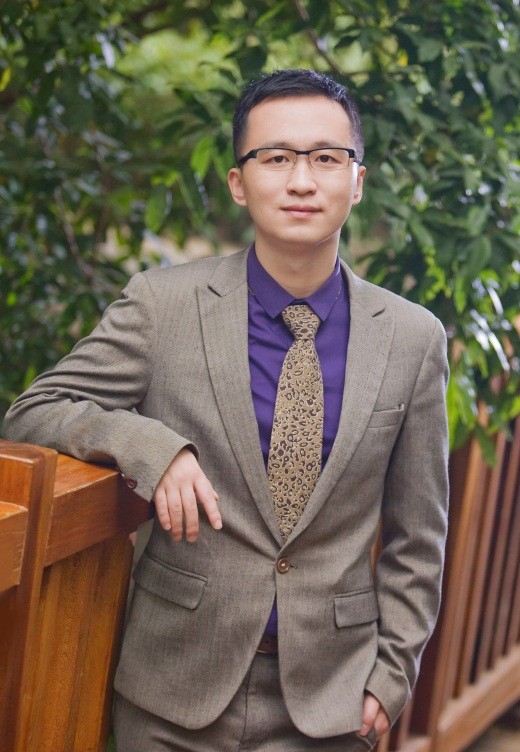

钟寰 Zhong Huan
博士,教授,环境生物专业
Ph.D,Professor,Environmental Biology
学术及社会兼职
(1) SCI期刊 Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 副主编(Associate Editor)
(2) 南京大学"中美环境研究中心" 副主任
(3) 南京大学环境学院国际交流工作助理
(4) 加拿大Trent大学环境与生命科学系(EnLS),兼职教授
(5) 第17届“国际环境重金属会议”(ICHMET)分会主席(6) 第33届“国际地球化学与环境健康会议”(SEGH)分会主席
(7) 第2届“生物废弃物环境修复国际会议”(BWS)分会主席
(8) SETAC亚太会议分会主席
(9) 南通市生态工程应用研究院科学顾问
(10)AECT副主编
Part-time Academic Job
(1) Associate Editor (Senior), Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology
(2)Associate Director, Sino-US Environmental Research Center, Nanjing University
(3) Dean Assistant for International Collaboration, School of Environment, Nanjing University
(4) Adjunct Faculty, Environmental and Life Science (EnLS), Trent University, Canada
(4) 17th ICHMET, Session chair
(5) 33th SEGH, Session chair
(6)2rd BWR, Session chair
(7) SETAC, Asia-Pacific, Session chair
荣誉 Honors
教育部高水平人才计划青年学者
Young Scholar of High Level Talent Project of Ministry of Education
首批江苏省优秀青年基金获得者
Science Fund for Outstanding Young Scholars, Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province
第十三批“江苏六大高峰人才”获得者
Six talent peaks project in Jiangsu Province
南京大学青年五四奖章
China's Youth Award, Nanjing University
江苏省青蓝工程优秀青年骨干教师
Young Scholar Award, Jiangsu Qinglan Project, Jiangsu Education Department
“江苏省科技创业大赛暨中国创新创业大赛(江苏赛区)”新能源及节能环保行业第二名,综合赛三等奖
泰州市双创大赛金奖
China Innovation and Entrepreneurship Competition: Jiangsu Province (3rd prize), Taizhou City (Gold award)
国际合作 International Collaboration
Wen-Xiong Wang(王文雄教授):Hong Kong Univ. Sci.Tech., HKSAR, China
Douglas Evans: Trent University, Canada
Holger Hintelman: Trent University, Canada
Ben Greenfield: University of California, Berkeley, US
Martin Tsui:University of North Carolina, US
Raymond Kwong:York University, Canada
Luis Nunes:Algarve University, PortugalYan Lin: Norwegian Institute for Water research (NIVA), Norway
教育背景
2004-2008: 香港科技大学大气海洋环境系AMCE 海洋环境科学 博士
2000-2004: 南京大学环境学院 环境科学 学士
Education
2004-2008 Ph.D Marine Environmental Science, HK Univ. Sci.Tech. , HKSAR, China
2000-2004: Bsc Environmental Science, Nanjing University, China
科研工作经历
2011.10─: 南京大学环境学院副教授(环境生物专业)
2009.01─2011.08: 博士后研究员,加拿大Trent大学
2008.09─2008.12: 助理研究员,香港科技大学生物系
Working Experience
2011-: Associate Professor, School of Environment, Nanjing University, China
2009-2011: Postdoc Fellow, ERS Progrom, Trent University, Canada
2008-2008: Research Assistant, Hong Kong Univ. Sci.Tech. , HKSAR, China
Contact
Email:zhonghuan@nju.edu.cn
Office: Room B413, School of Environment, Nanjing University (Xianlin Campus)
南京大学环境学院B413室, 南京大学仙林校区
LAB: Room A534, School of Environment, Nanjing University (Xianlin Campus)
南京大学环境学院A534室, 南京大学仙林校区
主持科研项目
Research projects

国家及省部级基金
1. 江苏省优秀青年基金:"稻田汞”的行为与风险研究
2. 国家自然科学基金面上项目:土壤水体成分对"稻田汞"的形态及水生生物有效性的影响研究
3.国家自然科学基金面上项目:秸秆还田稻田中汞活化的机理与影响因素研究
4. 江苏省自然科学基金:有机质对稻田中汞的水生生物可利用性影响研究
5. 教育部博士点基金:汞-土壤接触时间对稻田中汞的生物有效性影响研究6. 江苏省六大高峰人才计划:重金属污染土壤新型生态修复技术的研发与应用
7. 海外人员择优基金:有机质对稻田汞固定作用研究
8. 教育部、国家外专局“高端外国专家计划”中方负责人
National and Provincial Research Projects
1.Biogeochemistry and risk of mercury in rice paddy soils: Science Fund for Outstanding Young Scholars, Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (PI)
2.Effects of soil and water composition on the speciation and bioavailability of " paddy mercury" to aquatic organisms in rice paddy: National Natural Science Foundation of China (PI)
3.Mobilization of mercury in soil-rice systems under straw amendment: mechanisms and influencing factors: National Natural Science Foundation of China (PI)
4. Controls of organic matter on Hg bioavailability in soil-rice systems: Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (PI)
5. Effects of Hg-soil contact time on Hg bioavailability in paddy soils: Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (PI)
6. Novel technologies to remediate metal-contamianted soils: Six talent peaks project in Jiangsu Province (PI)
7. Immobilization of Hg by organic matter in paddy soils: Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars (PI)
8. Source Identification for Toxic Metals in China: High-End Foreign Experts Project (Chinese Coordinator)
— 科研成果—
Publications and Patents
同行评审论文 Peer-reviewed Papers
1. He LZ, Liu GX, Zhong H, Xu JM*. Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils by biochar: Mechanisms, potential risks and applications in China. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 846-855.
2. Lei P, Zhong H, Duan DD, Pan K*. A review on mercury biogeochemistry in mangrove sediments: hotspots of methylmercury production? Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 680:140-150.
3. Tang WL, Hintelmann H, Gu BH, Feng XB, Liu YR, Gao YX, Zhao JT, Zhu HK, Lei P, Zhong H*. Increased methylmercury accumulation in rice after straw amendment. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53:6144-6153.(封面文章)
4. Tang WL, Su Y, Gao YX, Zhong H*. Effects of Farming Activities on the Biogeochemistry of Mercury in Rice–Paddy Soil Systems. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2019, 102:635-642.
5. Lei P, Nunes LM, Liu YR, Zhong H*, Pan K*. Mechanisms of algal biomass input enhanced microbial Hg methylation in lake sediments. Environment International, 2019, 126:279-288.
6. Sheng F, Lin JY, Hong R, Jin X, Wang C, Zhong H, Gu XY, Gu C*. A new pathway of monomethylmercury photodegradation mediated by singlet oxygen on the interface of sediment soil and water. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 248:667-675.
7. Dang F, Li ZZ, Zhong H*. Methylmercury and selenium interactions: mechanisms and implications for soil remediation. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 10.1080/10643389.2019.1583051
8. Li YY#, Zhao JT#, Zhong H*, Wang YJ, Li H, Li YF , Liem-Nguyen V, Jiang T, Zhang ZY , Gao YX*, Chai ZF. Understanding Enhanced Microbial MeHg Production in Mining-Contaminated Paddy Soils under Sulfate Amendment: Changes in Hg Mobility or Microbial Methylators? Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53: 1844-1852.
9. Wang YJ, Dang F, Zheng XM*, Zhong H*. Biochar amendment to further reduce methylmercury accumulation in rice grown in selenium-amended paddy soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 365: 590-596.
10. Zhao JY, Ye ZH, Zhong H*. Rice root exudates affect microbial methylmercury production in paddy soils. Environmental Pollution, 2018. 242: 1921-1929.
11. Dang F, Jiang YY, Li M, Zhong H, Peijnenburg WJGM, Shi WL, Zhou DM*. Oral Bioaccessibility of Silver Nanoparticles and Ions in Natural Soils: Importance of Soil Properties. Environmental Pollution, 2018. 243: 364-373.
12. Gong Y, Nunes LM, Greenfield BK, Qin Z, Yang QQ, Huang L, Bu WB, Zhong H*. Bioaccessibility-corrected risk assessment of urban dietary methylmercury exposure via fish and rice consumption in China. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 630:222-230.
13. Zhang Y, Liu R-Y, Lei P, Wang Y-J, Zhong H*. Biochar and nitrate reduce risk of methylmercury in soils under straw amendment. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 619-620: 384-390.
14. Tang WL, Zhong H*, Xiao L*, Tan Q-G, Zeng Q-L, Wei Z-B. Inhibitory effects of rice residues amendment on Cd phytoavailability: A matter of Cd-organic matter interactions? Chemosphere, 2017, 186: 227-234.
15. Wang G, Liu H-Q, Gong Y, Wei Y, Miao A-J, Yang L-Y*, Zhong H*. Risk Assessment of Metals in Urban Soils from a Typical Industrial City, Suzhou, Eastern China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2017, 14(9), 1025. doi:10.3390/ijerph14091025
16. Peng Q, Greenfield B, Dang F, Gong Y, Bu W-B, Zhong H*. Mechanistic understanding of low methylmercury bioaccessibility from crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) muscle tissue. Science of the Total Environment. 2017, 603-604: 453-460.
17. Dang F, Li M, Zhu M, Zhong H, Hintelmann H, Zhou D-M*. Effects of exposure pathways on accumulation and phytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in soybean and rice seedlings. Nanotoxicology. 2017, 11: 699-709.
18. Wang G, Gong Y, Zhu Y-X, Miao A-J, Yang L-Y*, Zhong H*. Assessing the Risk of Hg Exposure Associated with Rice Consumption in a Typical City (Suzhou) in Eastern China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2017, 14(5), 525. doi:10.3390/ijerph14050525
19. Lin Y, Wang S-X*, Steindal EH, Zhang H, Zhong H, Tong Y-D, Wang Z-G, Braaten HFV, Wu Q-R, Larssen T. Minamata Convention on Mercury: Chinese Progress and Perspectives. National Science Review 2017, 4: 677-679.
20. Tang W-L, Evans D, Kraemer L, Zhong H*. Body size-dependent Cd accumulation in the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha from different routes. Chemosphere, 168: 825-831. 2017.
21. Tang W-L, Dang F, Evans D, Zhong H*, Xiao L*. Understanding reduced inorganic mercury accumulation in rice following selenium application: Selenium application routes, speciation and doses. Chemosphere, 169: 369-376. 2017.
22. Peng Q#, Nunes LM#, Greenfield BK, Dang F, Zhong H*. Are Chinese consumers at risk due to exposure to metals in crayfish? A bioaccessibility-adjusted probabilistic risk assessment. Environment International. 88:261-268.2016.
23. Shu R, Dang F, Zhong H*. Effects of incorporating differently-treated rice straw on phytoavailability of methylmercury in soil. Chemosphere 145:457-463. 2016.
24. Shu R, Wang Y-J, Zhong H*. Biochar amendment reduced methylmercury accumulation in rice plants. Journal of Hazardous Materials 313: 1–8. 2016.
25. Wang Y-J#, Dang F#, Evans D, Zhong H*, Zhao J-T, Zhou D-M. Mechanistic understanding of MeHg-Se antagonism in soil-rice systems: the key role of antagonism in soil. Scientific Reports 6:19477. 2016.
26. Wang Y-J, Dang F, Zhao J-T, Zhong H*. Selenium inhibits sulfate-mediated methylmercury production in rice paddy soil. Environmental Pollution 213: 232-239. 2016.
27. Zhu H-K, Zhong H*, Wu J-L. Incorporating rice residues into paddy soils affects methylmercury accumulation in rice. Chemosphere, 152: 259-264. 2016.
28. Wang Y-J, Dang F, Zhong H*, Wei Z-B, Li P. Effects of sulfate and selenite on mercury methylation in a mercury-contaminated rice paddy soil under anoxic conditions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 23:4602-4608. 2016.
29. Peng Q, Greenfield B, Dang F, Zhong H*. Human exposure to methylmercury from crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health. 38:169-181.2016.
30. Yong-Jie Wang, Zhong-Bo Wei, Qi-Long Zeng, Zhong H*. Amendment of sulfate with Se into soils further reduces methylmercury accumulation in rice. Journal of Soils and Sediments. 16: 2720-2727. 2016.
31. Dang F, Wang W-X, Zhong H, Wang S-Q, Zhou D-M*, Wang Y. Effects of phosphate on trace element accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.): a 5-year phosphate application study. Journal of Soils and Sediments. 16: 1440-1447. 2016.
32. Zhu D-W, Zhong H*, Zeng Q-L, Yin Y. Prediction of methylmercury accumulation in rice grains by chemical extraction methods. Environmental Pollution 199:1-9. 2015.
33. Zhu H-K, Zhong H*, Evans D, Hintelmann H. Effects of rice residue incorporation on the speciation, potential bioavailability and risk of mercury in a contaminated paddy soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials 293: 64–71. 2015.
34. Zhu H-K, Zhong H*, Fu F-J, Zeng Z. Incorporation of Decomposed Crop Straw Affects Potential Phytoavailability of Mercury in a Mining-Contaminated Farming Soil. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 95:254–259. 2015.
35. Zhu D-W, Zhong H*. Potential bioavailability of mercury in humus-coated clay minerals. Journal of Environmental Sciences 36:48-55. 2015.
36. Ma L, Zhong H*, Wu Y-G*. Effects of metal soil contact time on the extraction of mercury from soils. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 94:399–406. 2015.
37. Dang F, Zhao J, Greenfield BK, Zhong H, Wang YJ, Yang Z-S, Zhou D-M*. Soil geochemistry and digestive solubilization control mercury bioaccumulation in the earthworm Pheretima guillemi. Journal of Hazardous Materials 292:44-51. 2015.
38. Zhong H*, Kraemer L, Evans D. Influence of contact time and sediment composition on the bioavailability of Cd in sediments. Environmental Pollution 173: 11-16. 2013.
39. Zhong H*, Kraemer L, Evans D. Influence of body size on Cu bioaccumulation in zebra mussels Dreissena polymorpha exposed to different sources of particle-associated Cu. Journal of Hazardous Materials 261: 746-752. 2013.
40. Zhong H, Evans D, Wang W-X*. Uptake of Dissolved Organic Carbon-Complexed Cu-65 by the Green Mussel Perna viridis. Environmental Science and Technology 46: 2383-2390. 2012.
41. Zhong H*, Kraemer L, Evans D. Effects of aging on the digestive solubilization of Cu from sediments. Environmental Pollution 164: 195-203. 2012.
42. Zhong H, Wang W-X*. Controls of dissolved organic matter and chloride on mercury uptake by a marine diatom. Environmental Science and Technology 43: 8998-9003. 2009.
43. Zhong H, Wang W-X*. Inorganic mercury binding with different sulfur species in anoxic sediments and their gut juice extractions. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 28, 1851-1857. 2009.
44. Zhong H, Wang W-X*. The role of sorption and bacteria in mercury partitioning and bioavailability in artificial sediments. Environmental Pollution 157: 981-986. 2009.
45. Dang F, Zhong H, Wang W-X*. Copper uptake kinetics and regulation in a marine fish after waterborne copper acclimation. Aquatic Toxicology. 14: 238-244. 2009.
46. Zhong H, Wang W-X*. Effects of sediment composition on inorganic mercury partitioning, speciation and bioavailability in oxic surficial sediments. Environmental Pollution 151: 222-230. 2008.
47. Zhong H, Wang W-X*. Methylmercury extraction from artificial sediments by the gut juice of the sipunculan, Sipunculus nudus. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 27: 138-145. 2008.
48. Rainbow PS*, Amiard J-C, Amiard-Triquet C, Cheung M-S, Zhang L, Zhong H, Wang W-X. Trophic transfer of trace metals: subcellular compartmentalization in bivalve prey, assimilation by a gastropod predator and in vitro digestion simulations. Marine Ecology Progress Series 348: 125-138. 2007.
49. Zhong H, Wang W-X*. Metal-solid interactions controlling the bioavailability of mercury from sediments to the clams and sipunculans. Environmental Science and Technology 40: 3794-3799. 2006.
50. Zhong H, Wang W-X*. Sediment-bound inorganic Hg extraction mechanisms in the gut fluids of marine deposit feeders. Environmental Science and Technology 40: 6181-6186. 2006.
51. Zhong H, Wang W-X*. Influences of aging on the bioavailability of sediment-bound Cd and Zn to deposit-feeding sipunculans and soldier crabs. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 25: 2775-2780. 2006.
52. 赵家印,王永杰,钟寰*. 三种修复剂对稻米甲基汞富集的影响研究. 8: 284-289. 2019.
53. 杨倩琦,黄蕾*,布文博,龚雨,钟寰. 南京市人群膳食砷暴露健康风险研究. 环境卫生学杂志. 8: 191-196. 2018.
54. 张慧玲,党菲,李紫竹,钟寰*,王永杰*.土壤-植物系统“硒-汞拮抗”研究进展综述. 南京大学学报(自然科学). 53:903-911. 2017.
55. 张慧玲,刘玉荣,谷成*,钟寰*.秸秆还田影响汞污染地区“稻田汞”环境行为的研究进展. 科学通报. 62: 2717-2723. 2017.
56. 彭倩,朱慧可,钟寰*,贺美. 腐殖酸对汞污染稻田中甲基汞行为的影响.生态与农村环境学报. 31: 748-752. 2015.
57. 钟寰,王文雄*.沉积物中汞的生物可利用性研究进展. 环境化学. 30周年纪念专刊. 30: 165-178. 2011.
专利 Patents
- 钟寰,舒瑞. 2015. 一种利用有机碳降低水稻中甲基汞含量的方法.CN105170613A. Method capable of reducing content of methyl mercury content in rice through organic carbon.
- 钟寰,王永杰,党菲. 2015. 一种降低水稻甲基汞含量的方法.CN105052646A. Method capable of reducing content of methyl mercury content in rice.
学术会议报告 Conference Papers
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2005. Influences of contact time on the bioavailability of sediment-bound Cd and Zn. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) North America 26th Annual Meeting in Baltimore, MD, USA.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2006. Influences of sediment composition on Hg bioavailability from sediments as explained by Hg solid speciation. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) Asia/Pacific Meeting in Beijing, China.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2007. Key components controlling the partitioning, speciation, and bioavailability of inorganic mercury in anoxic sediments. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) North America 28th Annual Meeting in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2006. Influences of sediment composition on Hg bioavailability from sediments as explained by Hg solid speciation. The 2nd Marine Biological Association of Hong Kong (MBAHK) Postgraduate Symposium, Hong Kong.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2006. How contact time affects the bioavailability of sediment-bound heavy metals. International Conference on Contrasting Marine Ecosystems, Hong Kong.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2007. Bioavailability of sediment-bound methylmercury: a mechanistic study. The 5th international conference on marine pollution and ecotoxicology, Hong Kong.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2009. The roles of DOC and salinity in controlling the uptake of Hg and MeHg by a marine diatom. The 9th International Mercury conference, Guiyang, Guizhou, China
Dang F, Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2009. Copper uptake kinetics and regulation after waterborne copper pre-exposure in a marine fish. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) North America 30th Annual Meeting in New Orleans, LA, USA.
Zhong H, Wang X-X. 2011. Controls of different sorption on the partitioning and bioavailability of sedimentary mercury. The 10th International Mercury conference, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada.
Zhong H, Evans D, Wang W-X. 2012.Bioavailability of dissolved organic carbon-complexed 65Cu-DOC. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) World Congress, Berlin, Germany
Zhong H, Evans D, Wang W-X, Zhu H-K. 2012.Biological uptake of 65Cu-DOC complexes by the green mussel Perna viridis. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Zhu D-W, Zhong H. 2014. Prediction of methylmercury bioaccumulation in rice grains using (NH4)2S2O3 extraction method. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Zhang T, Han B-Y, Lu Y, Zhong H. 2014. Assessment of dietary metal exposure for residents in Nanjing city, China. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Peng Q, Greenfield B, Dang F, Zhong H. 2014. Mercury levels and potential dietary risk from crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in China. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Wang Y-J, Zhong H. 2014. Selenite and selenate into soils affect methylmercury accumulation in rice (Oryza sative L.). 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Zhu H-K, Zhong H. 2014. Influences of rice residual burial on speciation and bioavailability of mercury in a rice paddy soil. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Shu R, Tang W-L, Zhong H. 2015. Enhanced methylmercury accumulation in rice grains in contaminated paddy soils amended with rice straw. 12th International Conference on Mercury as a Global Pollutant (ICMGP).
Zhong H. 2015. Straw return increases methylmercury acumulation in rice grain. 1thInternational Institute for Environmental Studies Workshop (IIES).
Zhong H. 2016. Are consumers in China at risk due to exposure to metals in crayfish. 2nd international conference on Environmental Pollution and Health.
Zhong H. 2016. Dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-rice systems. 2nd International Institute for Environmental Studies Workshop.
Zhong H. 2016.Biogeochemistry and risk of Hg in contaminated soil-rice systems. 9th Sino-French joint lab 'Ecoland' workshop.
Zhong H. 2017. Dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-rice systems. Symposium of Ecotoxicology and Health Risk.
Zhong H. Understanding key factors controlling biogeochemistry and risk of mercury in contraminated soil-rice systems. The 3rd International Conference on Environmental Pollution and Health.
Zhong H. Effects of Biochar Amendment on MeHg Dynamics in Soil-Crop Systems. 2017. The 2nd International Conference on Biological Waste as Resource.
Zhong H. 2017. 汞生物地球化学与食品安全. 第一届中国青年汞论坛.
Zhong H. 2017. Effects of human activities on dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-crop systems. 33th SEGH.
Zhong H. 2017. Effects of human activities on dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-crop systems. 3rd International Institute of Environmental Studies Workshop (IIES 2017).
Zhong H. 2017. Effects of human activities on dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-crop systems. 13th International Conference on Mercury as a Global Pollutant (ICMGP 2017).
Zhong H. 2017. 1st IIES Graduate Student Forum, Asia. Sponsor.
学术会议报告 Conference Papers
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2005. Influences of contact time on the bioavailability of sediment-bound Cd and Zn. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) North America 26th Annual Meeting in Baltimore, MD, USA.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2006. Influences of sediment composition on Hg bioavailability from sediments as explained by Hg solid speciation. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) Asia/Pacific Meeting in Beijing, China.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2007. Key components controlling the partitioning, speciation, and bioavailability of inorganic mercury in anoxic sediments. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) North America 28th Annual Meeting in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2006. Influences of sediment composition on Hg bioavailability from sediments as explained by Hg solid speciation. The 2nd Marine Biological Association of Hong Kong (MBAHK) Postgraduate Symposium, Hong Kong.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2006. How contact time affects the bioavailability of sediment-bound heavy metals. International Conference on Contrasting Marine Ecosystems, Hong Kong.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2007. Bioavailability of sediment-bound methylmercury: a mechanistic study. The 5th international conference on marine pollution and ecotoxicology, Hong Kong.
Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2009. The roles of DOC and salinity in controlling the uptake of Hg and MeHg by a marine diatom. The 9th International Mercury conference, Guiyang, Guizhou, China
Dang F, Zhong H, Wang W-X. 2009. Copper uptake kinetics and regulation after waterborne copper pre-exposure in a marine fish. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) North America 30th Annual Meeting in New Orleans, LA, USA.
Zhong H, Wang X-X. 2011. Controls of different sorption on the partitioning and bioavailability of sedimentary mercury. The 10th International Mercury conference, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada.
Zhong H, Evans D, Wang W-X. 2012.Bioavailability of dissolved organic carbon-complexed 65Cu-DOC. The Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) World Congress, Berlin, Germany
Zhong H, Evans D, Wang W-X, Zhu H-K. 2012.Biological uptake of 65Cu-DOC complexes by the green mussel Perna viridis. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Zhu D-W, Zhong H. 2014. Prediction of methylmercury bioaccumulation in rice grains using (NH4)2S2O3 extraction method. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Zhang T, Han B-Y, Lu Y, Zhong H. 2014. Assessment of dietary metal exposure for residents in Nanjing city, China. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Peng Q, Greenfield B, Dang F, Zhong H. 2014. Mercury levels and potential dietary risk from crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in China. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Wang Y-J, Zhong H. 2014. Selenite and selenate into soils affect methylmercury accumulation in rice (Oryza sative L.). 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Zhu H-K, Zhong H. 2014. Influences of rice residual burial on speciation and bioavailability of mercury in a rice paddy soil. 17th International conference on heavy metals (ICHMET)
Shu R, Tang W-L, Zhong H. 2015. Enhanced methylmercury accumulation in rice grains in contaminated paddy soils amended with rice straw. 12th International Conference on Mercury as a Global Pollutant (ICMGP).
Zhong H. 2015. Straw return increases methylmercury acumulation in rice grain. 1thInternational Institute for Environmental Studies Workshop (IIES).
Zhong H. 2016. Are consumers in China at risk due to exposure to metals in crayfish. 2nd international conference on Environmental Pollution and Health.
Zhong H. 2016. Dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-rice systems. 2nd International Institute for Environmental Studies Workshop.
Zhong H. 2016.Biogeochemistry and risk of Hg in contaminated soil-rice systems. 9th Sino-French joint lab 'Ecoland' workshop.
Zhong H. 2017. Dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-rice systems. Symposium of Ecotoxicology and Health Risk.
Zhong H. Understanding key factors controlling biogeochemistry and risk of mercury in contraminated soil-rice systems. The 3rd International Conference on Environmental Pollution and Health.
Zhong H. Effects of Biochar Amendment on MeHg Dynamics in Soil-Crop Systems. 2017. The 2nd International Conference on Biological Waste as Resource.
Zhong H. 2017. 汞生物地球化学与食品安全. 第一届中国青年汞论坛.
Zhong H. 2017. Effects of human activities on dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-crop systems. 33th SEGH.
Zhong H. 2017. Effects of human activities on dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-crop systems. 3rd International Institute of Environmental Studies Workshop (IIES 2017).
Zhong H. 2017. Effects of human activities on dynamics and risk of Hg in soil-crop systems. 13th International Conference on Mercury as a Global Pollutant (ICMGP 2017).
Zhong H. 2017. 1st IIES Graduate Student Forum, Asia. Sponsor.
— 团队人员—
Personnel

唐雯莉
(Tang Wen-Li)
Assistant Professor
IIES Research Assistant Professor
Straw amendment-Hg biogeochemistry
雷沛
(Lei Pei)
Limnology & Biogeochemical Cycle & Passive sampling technique
研究方向:湖泊富营养化对污染物生物地球化学循环的驱动;被动采样技术的研发及应用
爱好:马拉松、越野
座右铭:人生如逆旅,我亦是行人
邮箱:leipei29@163.com

柳广霞
(Liu Guang-Xia)
BECT亚洲编辑部助理编辑
Assistant Editor of BECT Asian OfficeEffect of Biochar on Mercury Methylation Process in Sediments
研究方向:生物炭对沉积物汞甲基化过程的影响
邮箱:gxialiu@nju.edu.cn

李海龙
(Frank Lee)
2019级博 PhD student
Organic - Catamination induce methylation of Hg in paddy soil
研究方向:稻田土壤有机污染物诱导Hg甲基化过程
爱好:羽毛球

周洋
(Zhou Yang)
2020级博 PhD student
Free radical-mediated mercury degradation in rice fields
研究方向:稻田体系中自由基介导的汞循环
爱好:打游戏,打篮球
邮箱:zhouyangsms@163.com

张瑾
(Zhang Jin)
2020级直博 PhD student
Microbial Mercury Methylation
研究方向:微生物汞甲基化
爱好:手工、画画
邮箱:754382723@qq.com
座右铭:不以物喜,不以己悲

吴梦洁
(Wu Meng-Jie)
2021级博 PhD student
Accumulation and transformation of Hg in plants
研究方向:汞在植物中的累积和转化机制
爱好:旅游
邮箱:wumengjie0118@qq.com

张晓
(Zhang Xiao)
2022级博 PhD student
Rice paddy model for simulating Hg biogeochemistry

苏垚
(Su Yao)
2018级硕 Master student
Straw return -Hg biogeochemistry
研究方向:秸秆还田对稻田土壤汞甲基化的影响
爱好:游泳,轮滑,旅行
邮箱:807656326@qq.com

周航宇
(Zhou Hang-Yu)
2018级硕 Master student
Photodegradation of methylmercury in rice field systems
研究方向: 稻田上覆水中甲基汞光降解
爱好:健身、电影、打游戏
邮箱:770364929@qq.com

朱金杰
(Zhu Jin-Jie)
2018级硕 Master student
The role of algae decomposition to MeHg photodegradation
研究方向:藻类腐解对甲基汞光降解的影响
邮箱:1119670381@qq.com
爱好:看书、旅游
王文钦
(Wang Wen-Qin)
2018级硕 Master student
Fish and rice in dietary metal exposure
研究方向:鱼米摄食对重金属膳食暴露风险的影响
爱好:电影、音游
邮箱:2261308851@qq.com

梁宇
(Liang Yu)
2019级硕 Master student
Hg-Se antagonism in soil-rice systems
研究方向:稻田土壤系统中的硒汞拮抗
座右铭:做好自己,做好我们。
邮箱:byliangyuxy@yeah.net
杨亚楠
(Yang Ya-Nan)
2019级硕Master student
Photodegradation of methylmercury in paddy soil overlying water
研究方向:稻田上覆水甲基汞光降解
爱好:游泳,排球
邮箱:
oucyangyanan@126.com
邹楠
(Zou Nan)
2019级硕 Master student
Effects of organic matter on the bioavailability of mercury sulfide nanoparticles
研究方向:有机物对硫化汞纳米颗粒生物可利用性的影响
爱好:旅游、电影
邮箱:dreamoon98@outlook.com

储君茹
(Chu Jun-Ru)
2020级硕 Master student
Pesticide contamination of vegetables and solutions、Mercury in paddy field

孔雅琦
(Kong Ya-Qi)
2020级硕 Master student
Effects of specific inhibitors on microbial mercury methylation research

王佳琪
(Wang Jia-Qi)
2020级硕 Master student
Remediation of contaminated soil

让雪琦
(Rang Xue-Qi)
2020级硕 Master student
Remediation of contaminated soil

刘玉娇
(Liu Yu-Jiao)
2021级硕 Master student
Research on mercury in sewage sludge
研究方向:污泥汞的研究
爱好:摄影 电影
邮箱:1258537414@qq.com

李寿莹
(Li Shou-Ying)
2021级硕 Master student
Mercury biogeochemistry in rice fields
研究方向:稻田汞生物地球化学
爱好:跑步 阅读
邮箱:
lsy100415@163.com
李卓然
(Li Zhuo-Ran)
2021级硕 Master student
Effect of algae on methylmercury
研究方向:藻类对汞甲基化的影响
爱好:画画
邮箱:lzr549586726@163.com

赖盈杏
(Lai Ying-Xing)
2022级硕 Master student
Microbial mercury demethylation in lakes
研究方向:湖泊微生物去甲基化
爱好:漫画、美食、跳舞
邮箱:993230648@qq.com

周凡琪
(Zhou Fan-Qi)
2022级硕 Master student
Combined toxicity of the heavy metal mercury with other pollutants
研究方向:重金属汞与其它污染物的联合毒性
爱好:读书、看电影
邮箱:3203682969@qq.com

朱芮婕
(Zhu Rui-Jie)
2022级硕 Master student
Environmental behavior of heavy metals and microplastics
研究方向:重金属及微塑料的环境行为研究
爱好:咖啡,旅游,长跑,乐高
邮箱:2674566457@qq.com

宁文婧
(Ning Wen-Jing)
2023级博 PhD student
Biogeochemical processes of mercury in paddy ecosystems
研究方向:稻田生态系统汞的生物地球化学过程
爱好:滑板、乐高
邮箱:ningwenjing0616@outlook.com

陈家谊
(Chen Jia-Yi)
2024级硕 Master student
Studies of mercury exposure and its association with biological effects
研究方向:汞暴露及其与生物效应的关联研究
爱好:唱歌、散步、羽毛球
邮箱:jychen911@163.com

廖建南
(Liao Jian-Nan)
2023级硕 Master student
Mechanism of biological mercury enrichment in paddy soil
研究方向:秸秆对稻田土壤生物汞富集的影响
爱好:乒乓球、羽毛球
邮箱:2737242279@qq.com

张瀚天
(Zhang Han-Tian)
2024级硕 Master student
Effects of mercury on the greenhouse effect in wetland ecosystems
研究方向:汞对湿地生态系统温室效应的影响
爱好:篮球、健身、游戏
邮箱:1395906503@qq.com

胡杨
(Hu Yang)
2023级硕 Master student
Migration and evolution of methylmercury in paddy fields
研究方向:稻田甲基汞的迁移和衍变
爱好:散步、小提琴
邮箱:hyadg112358@163.com

王永杰
(Wang Yong-Jie)
联合培养
Hg-Se antagonism in soil-rice systems
研究方向:1.土壤/沉积物生物地球化学氧化还原过程中碳、氮、磷、硫、有害痕量金属及非金属的迁移、转化及生物可利用性。
2.同位素地球化学。

赵浩然
(Zhao Hao-Ran)
2023级硕 Master student
Marine alge-methylmercury model
研究方向:海洋藻类-甲基汞模型
爱好:打篮球,健身,看电影
邮箱:1435112048@qq.com

柳敬丽
(Liu Jing-Li)
Marine microbiology
研究方向:海洋微生物
邮箱:jingliliu91@163.com
李紫竹
(Li Zi-Zhu)
2017级硕 Master student
Hg-Se antagonism in soil-rice systems
研究方向:1.土壤中硒对汞的作用机制。2.全国稻田土中汞甲基化的主控因素。
爱好:旅游、音乐、游戏

秦榛
(Qin Zhen)
2017级硕 Master student
Human exposure and health risk assessment
研究方向:重金属食品安全与人体健康风险(中药)
爱好:二胡,cosplay,动漫
座右铭:本来就擅长沉默,失败后更应坚守。

唐朝
(Tang Chao)
2017级硕 Master student
Sulfate added-Mercury methylation
研究方向:外源硫输入对稻田土壤汞甲基化的调控机制研究
爱好:小提琴等
赵家印
(Zhao Jia-Yin)
2015级硕 Master student
Mercury contaminated soil remediation
研究方向:1.水稻栽种对土壤甲基汞行为的影响。2.汞污染农田土壤修复。
爱好:打球,跑步,三国杀,狼人杀,竞技类游戏等

夏振江
(Xia Zhen-Jiang)
助理研究员
Research Assistant Professor
Safety evaluation of mercury-containing drugs and environmental pollutants
研究方向:1.含汞传统药物的安全性和健康风险评估
2.环境污染物的体内和体外健康风险评估模型的建立
张悦
(Zhang Yue)
2015级硕 Master student
Microbial methylation of mercury
研究方向:1.秸秆还田对水稻镉生物可利用性的影响
2.甲基化细菌对沉积物中汞甲基化的影响
爱好:旅游、看电影
箱:18856014218@163.com

龚雨
(Gong Yu)
2015级硕 Master student
Human exposure and health risk assessment
孙立平
(Oliver Sun)
在职研究生 Master student
Soil remediation
研究方向:汞污染土壤修复
座右铭:无论世界如何,内心需有一丝纯粹,一点追求,一个梦想

吴非凡
(Wu Fei-Fan)
2015级本科生 UG student
中药中重金属含量检测与风险评估
创新计划小组组长
兴趣爱好:摄影、跑步
座右铭:参差多态乃是幸福本源。

陈宗娅
(Chen Zong-Ya)
联合培养
2014级硕 Mphil
Straw amendment-Hg biogeochemistry
研究方向:不同秸秆还田方式对轮种情况下稻田土壤与作物中汞的影响
座右铭:车到山前必有路,没有到不了的远方
爱好:旅游,逛街,看电影
毕业去向:环保单位

舒瑞
(Rick)
2013级硕 Mphil
Soil remediation
研究方向:稻田汞污染土壤修复
爱好:三国杀,羽毛球,游泳,旅游,打牌,游戏
邮箱:244654741@qq.com
毕业去向:江苏润环

朱慧可
(Zhu Hui-Ke)
2012级硕 Mphil
Straw amendment-Hg biogeochemistry
研究方向:秸秆还田对矿区稻田汞生物地球化学影响研究
爱好:球类运动,音乐
毕业去向:环保单位

朱代文
(Zhu Dai-Wen)
2012级硕 Mphil
Hg biogeochemistry in soil-rice systems
研究方向:1.不同水稻品种汞和镉富集及转运机制研究
2.稻田汞生物富集,化学萃取方法预测稻田甲基汞的生物富集

彭倩
(Peng-Qian)
2012级硕 Mphil
Human exposure and health risk assessment
研究方向:食品重金属污染及健康风险评估
邮箱:1063611747@qq.com
毕业去向:常州环科院

马岚
(Sunny)
联合培养
2011级硕 Mphil
兴趣爱好:篮球,画画
星座:射手座
座右铭:Where there is a will, there is a way.
毕业去向:加拿大Trent大学博士生

马乐星
(Ma Yue-Xing)
2010级本科生 Bachelor
Effects of contact time on metal bioavailability in soils
创新计划小组组长
国家级大学生创新研究计划:接触时间对稻田土壤中重金属生物可利用性的影响,2012-2013

曹晨
(Cao Chen)
2010级本科生 Bachelor
Effects of contact time on metal bioavailability in soils
创新计划小组成员
国家级大学生创新研究计划:接触时间对稻田土壤中重金属生物可利用性的影响,2012-2013

王楚楚
(Wang Chu-chu)
2010级本科生 Bachelor
Effects of contact time on metal bioavailability in soils
创新计划小组成员
国家级大学生创新研究计划:接触时间对稻田土壤中重金属生物可利用性的影响,2012-2013
毕业去向:南京大学推免生

郭琼
(Guo Qiong)
2010级本科生 Bachelor
Effects of contact time on metal bioavailability in soils
创新计划小组成员
国家级大学生创新研究计划:接触时间对稻田土壤中重金属生物可利用性的影响,2012-2013
毕业去向:南京大学推免生

韩碧瑶
(Han Bi-Yao)
2011级本科生 Bachelor
Human exposure and health risk assessment
创新计划小组组长
国家级大学生创新研究计划:南京居民膳食中重金属暴露风险,2013-2015

张婷
(Zhang Ting)
2011级本科生 Bachelor
Human exposure and health risk assessment
创新计划小组组长
国家级大学生创新研究计划:南京居民膳食中重金属暴露风险,2013-2015
毕业去向:北京大学推免生

卢艺
(Lu Yi)
2011级本科生 Bachelor
Human exposure and health risk assessment
创新计划小组成员
国家级大学生创新研究计划:南京居民膳食中重金属暴露风险,2013-2015

于文汐
(Yu Wen-Xi)
2012级本科生 Bachelor
Straw amendment-Hg biogeochemistry
创新计划小组组长
国家级大学生创新研究计划:秸秆还田对水稻汞富集影响探究,2014-2016

方元狄
(Fang Yuan-Di)
2012级本科生 Bachelor
Straw amendment-Hg biogeochemistry
创新计划小组成员
国家级大学生创新研究计划:秸秆还田对水稻汞富集影响探究,2014-2016

吴嘉璐
(Wu Jia-Lu)
2012级本科生 Bachelor
Straw amendment-Hg biogeochemistry
创新计划小组成员
国家级大学生创新研究计划:秸秆还田对水稻汞富集影响探究,2014-2016

张思凡
(Zhang Si-Fan)
2012级本科生 Bachelor
Straw amendment-Hg biogeochemistry
创新计划小组成员
国家级大学生创新研究计划:秸秆还田对水稻汞富集影响探究,2014-2016

周燕
(Zhou Yan)
2012级本科生Bachelor
Global warming on Hg biogeochemistry
创新计划小组组长
国家级大学生创新研究计划:“温室效应——水稻汞富集“探索,2013-2015

王阳明
(Wang Yang-Ming)
2012级本科生 Bachelor
Global warming on Hg biogeochemistry
创新计划小组成员
国家级大学生创新研究计划:“温室效应——水稻汞富集“探索,2013-2015

姜琳淼
(Jiang Lin-Miao)
2012级本科生 Bachelor
Global warming on Hg biogeochemistry
创新计划小组成员
国家级大学生创新研究计划:“温室效应——水稻汞富集“探索,2013-2015

施沁人
(Shi Qin-Ren)
2013级本科生 Bachelor
Food Safety: Informationization and Visualization
创新计划小组组长
省级大学生创新研究计划:食品安全信息及可视化研究

胡子怡
(Hu Zi-Yi)
2013级本科生 Bachelor
Food Safety: Informationization and Visualization
创新计划小组成员
省级大学生创新研究计划:食品安全信息及可视化研究

杨倩
(Yang Qian)
2013级本科生 Bachelor
Food Safety: Informationization and Visualization
创新计划小组成员
省级大学生创新研究计划:食品安全信息及可视化研究

张颜
(Zhang Yan)
2014级本科生 Bachelor
Hg-Se antagonism in soil-rice systems
获加拿大MITACS资助
大学生创新创业计划项目
Science & Technology Competition and Innovation &Entrepreneurship Training Programs (STC Program)

Effects of contact time on metal bioavailability in soils
国家级大学生创新研究计划:接触时间对稻田土壤中重金属生物可利用性的影响,2012-2013,获最高全额研究资助(2万)
国家级创新计划
组长: 马乐星
成员:2010级本科生(马乐星、郭琼、王楚楚、曹晨)
进展:已结题

Assessing dietary exposure tometals for NanJing residents
国家级大学生创新研究计划:南京居民膳食中重金属暴露风险,2013-2015获最高全额研究资助(2万),获全额资助参与第17届“国际环境重金属会议”(ICHMET)并演讲
国家级创新计划
组长: 张婷
成员:2011级本科生(张婷、韩碧瑶、卢艺)
进展:已结题

Effects of global warming on Hg accumulation in rice
国家级大学生创新研究计划:“温室效应”--“水稻汞富集”探索,2013-2015,获最高全额研究资助(2万)
国家级创新计划
组长: 周燕
成员:2012级本科生(周燕、王阳明、姜琳淼)
进展:已结题
成果:周燕,王永杰曾其龙等,不同水稻品种汞富集及转运机制探索[EB/OL].北京:中国科技论文在线 [2016-05-19]. http://www.paper.edu.cn/releasepaper/content/201605-694

Effects of straw amendment on Hg accumulation in rice
国家级大学生创新研究计划:“秸秆还田对水稻富集影响研究”,2014-2016,获最高全额研究资助(2万)
国家级创新计划
组长: 于文汐
成员:2012级本科生(于文汐、张思凡、方远狄、吴嘉璐)
进展:已结题
成果:Zhu H-K, Zhong H, Wu J-L. 2016. Incorporating rice residues into paddy soils affects methylmercury accumulation in rice Chemosphere 152:259-264.2016
Food Safety: Informationization and Visualization
省级大学生创新研究计划:食品安全信息及可视化研究
省级创新计划
组长: 施沁人
成员:2013级本科生(施沁人、杨倩、胡子怡)
进展:已结题
成果:“挑战杯”三等奖 (校级)
创新计划课题:中药中重金属含量检测与风险评估(2016-2017)
国家级创新计划
组长: 吴非凡
成员:2015级本科生(吴非凡、周叶、王志强、肖润民)
— 课题组风采 —
Galleries
联系我们
Contact Info

Email:zhonghuan@nju.edu.cn

Call:025-89680316
Address:南京市栖霞区仙林大道163号南京大学环境院B413室

Lab:南京大学环境学院A534
Graduate office:南京大学环境学院A544
留言板
Messages for us